Conditional Statements Tutorial
More Advanced
Boolean Expressions
You can combine the operators "Not", "And"
and "Or" in
the same boolean expression, using the parentheses "(" and
")"
For example:
(True And False) Or (Not False) = True
Figure 5
| (True And False) |
Or |
(Not False) |

False |

Or |

True |

True |
The priority of the "Not"
operator is higher than
the priority of "And" and "Or" operators.
For
example:
Not True And False = False, because
The first operater to be
executed is the "Not" (Figure 6):
Not True =
False.
Then we get the following boolean expression:
False And False =
False.
Figure 6
| Not True |
And |
False |

False |

And |

False |

False |
If
we will executed the "And" operator before
the "Not" operator,
we would get WRONG answer (Figure
7).
Figure 7
| Not |
True And False |

Not |

False |

True |
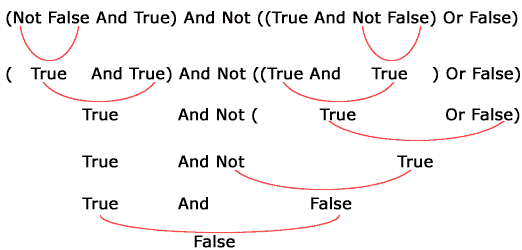
A Teaser:
What will be printed on
the form after
executing the following code?
Dim Elvis As
Boolean
Elvis = (Not False And True) And Not ((True And Not False) Or
False)
Print Elvis
Answer: